Video lecture for this chapter
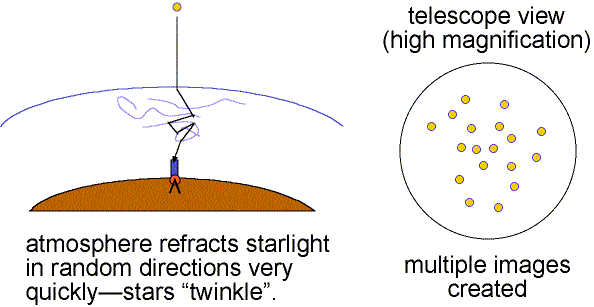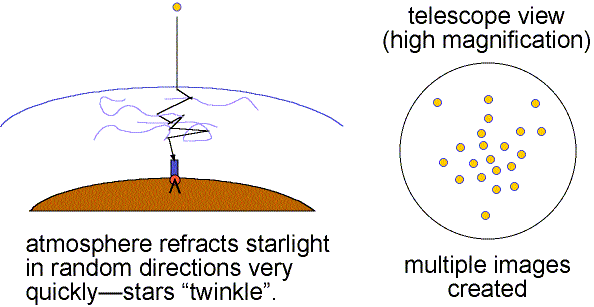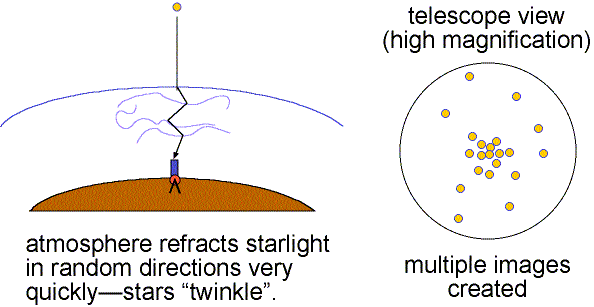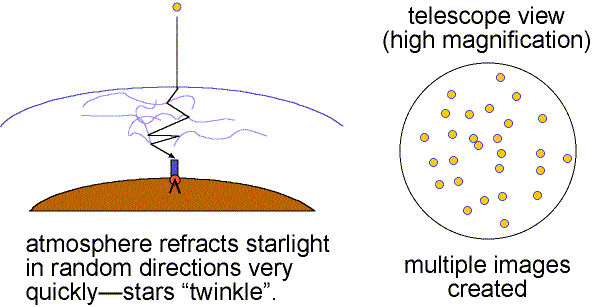
The air is constantly in turbulent motion and light from celestial objects is bent randomly in many ways over time periods of tens of milliseconds. Images dance about (twinkle) and images are blurred. The atmospheric blurring distorts the view of astronomical objects much as ripples in water distort the objects below the surface. This atmospheric effect is called seeing.

Good seeing is when the air is stable (little turbulence) and the twinkling is small. Details as small as 0.5 arc seconds can be seen when the seeing is good (still much larger than the theoretical resolving power of large research telescopes). Poor seeing happens when the air is turbulent so the images dance about and details smaller than 2 to 3 arc seconds cannot be seen. The more atmosphere there is above a telescope, the greater is the turbulent motion and the poorer is the seeing. This is one reason why research telescopes are located on very high mountains.
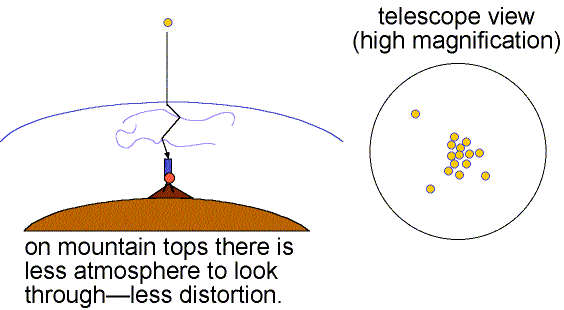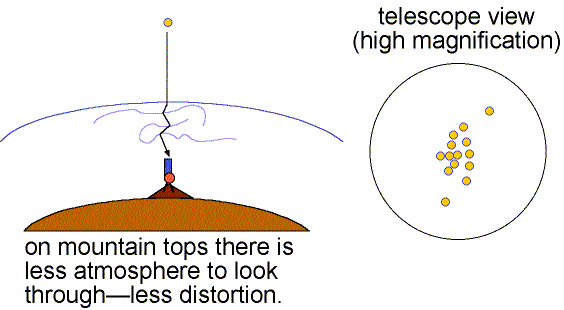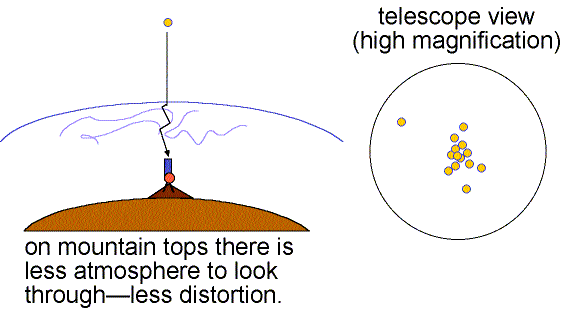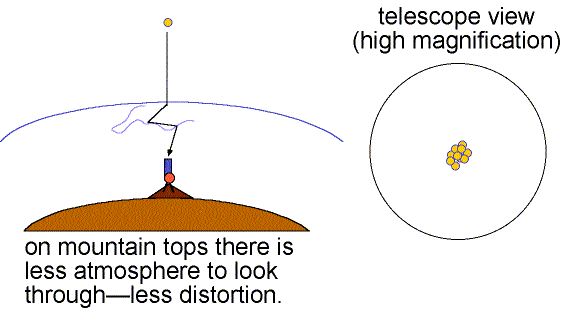
Speckle interferometry can get rid of atmospheric distortion by taking many fast exposures of an object. Each fraction-of-a-second exposure freezes the motion of the object. Extensive computer processing then shifts the images to a common center and removes other noise and distortions caused by the atmosphere, telescope, and electronics to build up a distortion-free image. See Steven Majewski's lecture notes on speckle for further exploration of speckle interferometry. Another technique called adaptive optics makes quick changes in the light path of the optics to compensate for the atmospheric turbulence. Before the focused light from the objective reaches the camera, it bounces off a thin deformable mirror that can be adjusted thousands of times a second to reposition the multiple images back to the center. A site to explore this topic further is the Center for Adaptive Optics website. Also see the UCLA Galactic Center Group's work made possible by adaptive optics imaging of our galaxy's center. The GIF animation below shows the great improvement that adaptive optics can provide.
Telescopes in orbit like the Hubble Space Telescope are above the turbulent effect of the atmosphere and can achieve their theoretical resolving power. The Hubble Space Telescope has a 2.4-meter objective, making it the second-largest telescope ever put in orbit (the James Webb Space Telescope with a 6.5-meter objective deployed in 2022 is now the largest and the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will be same size as Hubble). One major drawback to satellite observatories is the large cost to build and maintain them. Adaptive optics on ground-based telescopes now can remove the seeing effects on small patches of the sky at a time and enable the huge research telescopes to take even sharper pictures than those from the Hubble Space Telescope.
![]() Go back to previous section --
Go back to previous section --
![]() Go to next section
Go to next section
last updated: January 20, 2022