Sections Review
Video lecture for this chapter
This material (including images) is copyrighted!.
See my copyright notice for fair use
practices.
Vocabulary
| absorption line spectrum | continuous spectrum |
discrete spectrum |
| emission line spectrum | luminosity | Stefan-Boltzmann
law |
| thermal spectrum | Wien's law |
Formulae
- Wien's Law:
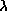 peak
= 2.9 × 106/temperature. The units of the peak wavelength are
nanometers and the temperature is in Kelvin.
peak
= 2.9 × 106/temperature. The units of the peak wavelength are
nanometers and the temperature is in Kelvin.
- Stefan-Boltzmann Law: Energy emitted by a square meter on an object's
surface =
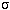 ×temperature4,
where
×temperature4,
where 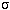 is a constant of nature.
is a constant of nature.
- What are the three basic kinds of spectrum? Can an object produce more
than one type at the same time?
- What produces a thermal spectrum? Does it depend on chemical
composition?
- How can temperature be determined from a continuous spectrum? How would
the color of a hot object compare to the color of a cooler object? At what
wavelength do you at 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit radiate the most? (Hint: use the
temperature scales table.)
- How will the thermal spectrum produced by a chunk of lead compare
to the thermal spectrum produced by a chunk of iron of the same size and temperature?
- What produces an emission line spectrum? Do
you need a thermal source in the background?
- Can you see emission lines if a thermal source is in
the background? What does their visibility depend on? (Think about the
temperature of the gas producing the emission lines and the temperature of the
the background thermal source.)
- What produces an absorption line spectrum? Do
you need a thermal source? Would you see absorption lines if the gas in front
of a thermal source was hotter than the thermal source? Explain why.
- Why must you use a pattern of lines to find the composition? Why is
one line not sufficient?
- What kind of spectrum and what pattern of lines would you see if you
heated up a tube filled with hydrogen, helium and neon gas?
 Go back to previous section --
Go back to previous section --
 Go to next section
Go to next section
last updated: 17 May 2001
Is this page a copy of Strobel's
Astronomy Notes?
Author of original content:
Nick Strobel
![]() Go back to previous section --
Go back to previous section --
![]() Go to next section
Go to next section